DAC Vs. AOC: How To Choose The Best Networking Cable
Why Cable Choice Matters in Modern Networking
The foundation of any reliable, high-speed network lies in its connectivity infrastructure. With increasing demands for faster data transfer, efficient energy usage, and seamless scalability, selecting the right type of cable is more important than ever.
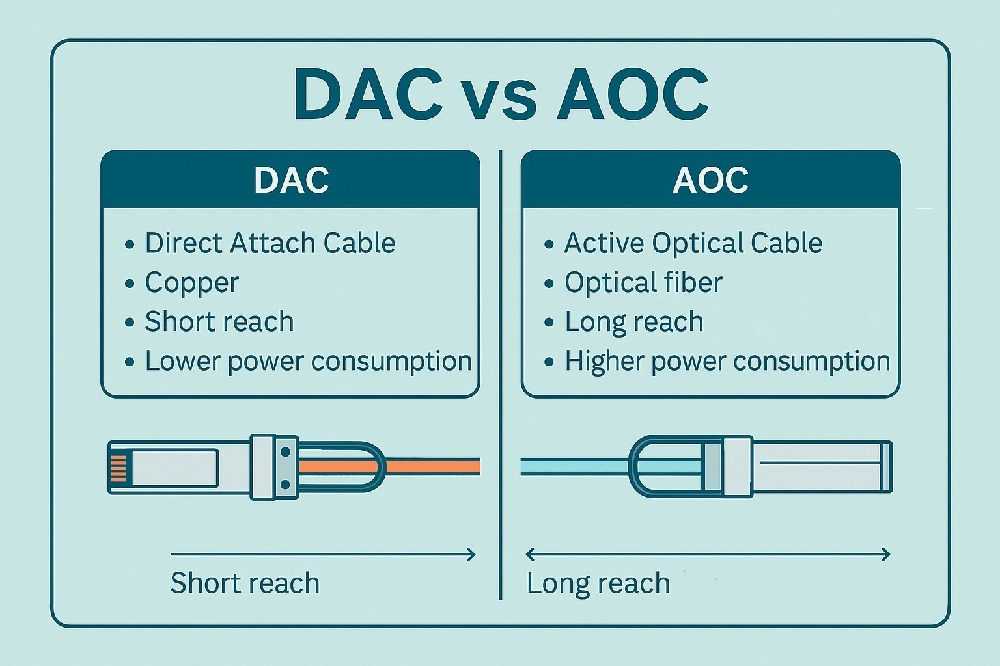
Two commonly used interconnect solutions in networking are Direct Attach Cables (DAC) and Active Optical Cables (AOC). While both serve to link critical components like servers, switches, and storage devices, they cater to different needs. This guide will help you make an informed decision by diving deeper into their features, benefits, and practical applications.
- Understanding Direct Attach Cables in Detail
- Diving Deeper into Active Optical Cables
- Expanded Comparison: DAC vs AOC
- Key Factors for Decision - Making
- Practical Use Cases
- FAQ
- Conclusion
Understanding Direct Attach Cables (DAC) in Detail
Direct Attach Cables (DACs) are high-speed copper-based cables with fixed transceiver modules at each end. Widely used in small to medium-sized data centers, they provide a low-cost solution for short-range connections.
Features of DACs:
- Material: Constructed with high-quality copper wiring.
- Length: Most commonly available in lengths between 0.5 and 7 meters.
- Variants: Comes in two forms:
- Passive DAC: No built-in signal amplification, suitable for shorter distances.
- Active DAC: Includes signal amplification for slightly extended distances.
Advantages of DACs:
Cost-Effective Deployment:
Copper cables are less expensive to manufacture and implement, making DACs a budget-friendly choice for short-range applications.Low Latency Performance:
DACs transmit electrical signals directly, minimizing the latency compared to optical counterparts.Energy Efficiency:
Passive DACs, in particular, require no external power, contributing to lower overall energy consumption in your data center.Ease of Maintenance:
Plug-and-play design simplifies installation and reduces the time needed for troubleshooting and upgrades.
Limitations of DACs:
- Limited reach: Maximum reliable distance is around 7 meters.
- Heavier and bulkier than optical cables, which can complicate cable management in dense setups.
- Susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI), which can degrade signal quality in high-EMI environments.
Diving Deeper into Active Optical Cables (AOC)
Active Optical Cables (AOCs) employ optical fibers for data transmission and include integrated optoelectronic components that convert electrical signals into light for faster, long-distance communication.
Features of AOCs:
- Material: Lightweight and flexible optical fibers.
- Length: Can cover distances of up to 150 meters, depending on the design and network standards.
- Signal Transmission: Uses light to carry data, which ensures minimal signal loss even over extended lengths.
Advantages of AOCs:
Extended Distance:
Ideal for larger data centers or interconnecting systems across floors or buildings.Higher Bandwidth:
Optical fibers support higher data rates (e.g., 10Gbps, 40Gbps, 100Gbps) without sacrificing signal integrity.Resistance to EMI:
AOCs are immune to electromagnetic interference, making them ideal for noisy environments.Lightweight and Flexible:
Optical fibers are easier to route through tight spaces, aiding in efficient cable management.
Limitations of AOCs:
- Higher upfront cost compared to DACs.
- Requires power to operate the optoelectronic components.
- Fragility: Optical fibers are more delicate and require careful handling during installation.
Expanded Comparison: DAC vs. AOC
Key Factors for Decision-Making
1. Distance Requirements:
- Use DAC for short connections within a rack or between adjacent racks.
- Use AOC for longer connections across rooms or between network zones.
2. Performance Needs:
- Low Latency Applications: If latency is critical, such as in financial services or high-performance computing, DAC is the better choice.
- High Bandwidth Demands: Opt for AOC for tasks involving AI, big data, or large-scale video streaming.
3. Budget:
- Cost-Conscious Projects: DACs are ideal for tight budgets and can reduce initial deployment costs.
- Investment in Future-Proofing: AOCs may have a higher upfront cost but offer scalability and better long-term performance.
4. Environment:
- In high-EMI areas, such as industrial facilities, AOCs outperform DACs due to their immunity to interference.
5. Maintenance and Scalability:
- DAC: Easier to replace and maintain for short-term needs.
- AOC: Lighter and more manageable for large installations with complex routing.
Practical Use Cases
When to Use DAC:
- Connecting servers and switches within a rack.
- Small to medium-sized data centers where budget constraints are significant.
- Latency-sensitive environments with minimal EMI concerns.
Photo by Taylor Vick on Unsplash
When to Use AOC:
- Long-range data transfer in large data centers or campus networks.
- High-performance environments demanding maximum bandwidth.
- Industrial setups prone to EMI.
FAQs About DAC and AOC
Q: Can DACs and AOCs be used interchangeably?
No, the choice depends on the distance, performance, and environmental requirements. DACs are optimal for short distances, while AOCs excel at longer connections.
Q: Are there hybrid solutions?
Yes, some systems combine both DAC and AOC for different parts of the network, leveraging the strengths of each cable type.
Q: How can I future-proof my choice?
Consider your network's scalability. If you anticipate significant growth or bandwidth demands, investing in AOCs might be a better long-term strategy.
Q: Can DACs and AOCs be used with different vendors equipment at each end?
While DACs and AOCs were originally designed to be used with the same vendors equipment end to end, the T Optics line of cables can be custom coded at each end to work with the equipment you need them to.
Conclusion: Finding the Right Fit
The decision between Direct Attach Cables (DAC) and Active Optical Cables (AOC) is not about which is better but which is more suited to your specific needs. Factors like distance, budget, performance requirements, and environmental conditions should guide your choice.
Summary:
- Use DACs for short, cost-effective, and low-latency connections.
- Use AOCs for long-distance, high-bandwidth, and EMI-resistant setups.
By thoroughly evaluating your current needs and future goals, you can select the ideal networking cable to ensure seamless connectivity and performance.
Take advantage of our limited time offer on all your direct attach cable requirements while available:




.jpg)

.jpg)
